Difference between revisions of "Input Plugin"
(→Syntax) |
(→Syntax) |
||
| Line 86: | Line 86: | ||
| <code>input</code> || <code>string</code> || <code>""</code> || '''Yes''' || | | <code>input</code> || <code>string</code> || <code>""</code> || '''Yes''' || | ||
The input that should be processed. | The input that should be processed. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
|- | |- | ||
| <code>credentials</code> || <code>void</code> || n/a || No || | | <code>credentials</code> || <code>void</code> || n/a || No || | ||
Revision as of 09:51, 23 February 2024
This is a special interaction plugin that allows you to handle complex and multilingual inputs for special use cases (e.g. entering user names/passwords, performing search queries, etc.). In order to use this plugin, a corresponding content service must be implemented that processes the entered input (e.g. by evaluating an input parameter). The plugin can be used with version 0.1.123 or higher.
Usage[edit]
The plugin must be loaded with a content service URL that is able to process the input (which is generally set as input URL parameter). Optionally, a type, a default language, a headline, a background, an extension, and/or a hint can be set. Please see following action syntax examples.
content:request:interaction:{URL}@http://msx.benzac.de/interaction/input.htmlcontent:request:interaction:{URL}|{TYPE}@http://msx.benzac.de/interaction/input.htmlcontent:request:interaction:{URL}|{TYPE}|{DEFAULT_LANG}@http://msx.benzac.de/interaction/input.htmlcontent:request:interaction:{URL}|{TYPE}|{DEFAULT_LANG}|{HEADLINE}@http://msx.benzac.de/interaction/input.htmlcontent:request:interaction:{URL}|{TYPE}|{DEFAULT_LANG}|{HEADLINE}|{BACKGROUND}@http://msx.benzac.de/interaction/input.htmlcontent:request:interaction:{URL}|{TYPE}|{DEFAULT_LANG}|{HEADLINE}|{BACKGROUND}|{EXTENSION}@http://msx.benzac.de/interaction/input.htmlcontent:request:interaction:{URL}|{TYPE}|{DEFAULT_LANG}|{HEADLINE}|{BACKGROUND}|{EXTENSION}|{HINT}@http://msx.benzac.de/interaction/input.html
The {TYPE} part can be set to one of the following values.
default: Default inputsecret: Secret input (this type can be used for passwords and hides the input by default)search: Search input (this type can be used for search queries and automatically submits the input 3 seconds after it has been changed)
The {DEFAULT_LANG} part can be set to one of the following values.
en: English keyboard layoutfr: French keyboard layoutde: German keyboard layoutes: Spanish keyboard layoutpt: Portuguese keyboard layoutit: Italian keyboard layouttr: Turkish keyboard layoutru: Russian keyboard layout
Please note that the keyboard layout can also be changed at runtime.
The content service URL should contain the keyword {INPUT}, which is replaced with the corresponding value. Please see following action syntax examples.
content:request:interaction:http://link.to.input.handler?input={INPUT}@http://msx.benzac.de/interaction/input.htmlcontent:request:interaction:http://link.to.input.handler?input={INPUT}|default@http://msx.benzac.de/interaction/input.htmlcontent:request:interaction:http://link.to.input.handler?input={INPUT}|secret|en@http://msx.benzac.de/interaction/input.htmlcontent:request:interaction:http://link.to.input.handler?input={INPUT}|search|fr|Titre@http://msx.benzac.de/interaction/input.htmlcontent:request:interaction:http://link.to.input.handler?input={INPUT}|default|de|Überschrift|http://link.to.image@http://msx.benzac.de/interaction/input.htmlcontent:request:interaction:http://link.to.input.handler?input={INPUT}|secret|es|Titular|http://link.to.image|Extensión@http://msx.benzac.de/interaction/input.htmlcontent:request:interaction:http://link.to.input.handler?input={INPUT}|search|pt|Título|http://link.to.image|Extensão|Texto de dica@http://msx.benzac.de/interaction/input.htmlcontent:request:interaction:http://link.to.input.handler?input={INPUT}||it|Titolo@http://msx.benzac.de/interaction/input.htmlcontent:request:interaction:http://link.to.input.handler?input={INPUT}||tr|Başlık||Eklenti@http://msx.benzac.de/interaction/input.htmlcontent:request:interaction:http://link.to.input.handler?input={INPUT}||ru|Заголовок|||Текст подсказки@http://msx.benzac.de/interaction/input.html
The content service should return either an action property to be executed (e.g. for user logins) or a template and items property to display the results (e.g. for search queries). Please see this example code how a user login response can look like.
{
"action": "reload"
}
The next example code shows how a search query response can look like.
{
"headline": "{ico:search} \"Video\"",
"template": {
"type": "separate",
"layout": "0,0,2,4",
"icon": "msx-white-soft:movie",
"color": "msx-glass"
},
"items": [{
"title": "Video 1",
"playerLabel": "Video 1",
"action": "video:http://msx.benzac.de/media/video1.mp4"
}, {
"title": "Video 2",
"playerLabel": "Video 2",
"action": "video:http://msx.benzac.de/media/video2.mp4"
}, {
"title": "Video 3",
"playerLabel": "Video 3",
"action": "video:http://msx.benzac.de/media/video3.mp4"
}]
}
Please note that for responses that contain a template and items property, the properties headline, extension, background, and hint will also be used (and will replace potential initial values). Please also note that the content is compressed (i.e. the layout grid size is 16x8).
If you would like to use the plugin as reference to implement your own plugin, please have a look at this implementation script: http://msx.benzac.de/interaction/js/input.js.
Note: Currently, the input plugin cannot be used with panels. Please also note that all requests to the content service are HTTP GET requests.
Syntax[edit]
| Parameter | Type | Default Value | Mandatory | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
input |
string |
"" |
Yes |
The input that should be processed. |
credentials |
void |
n/a | No |
A keyword that indicates that user credentials (e.g. cookies, authorization headers, etc.) are enabled for content service requests. Technically, this keyword sets the |
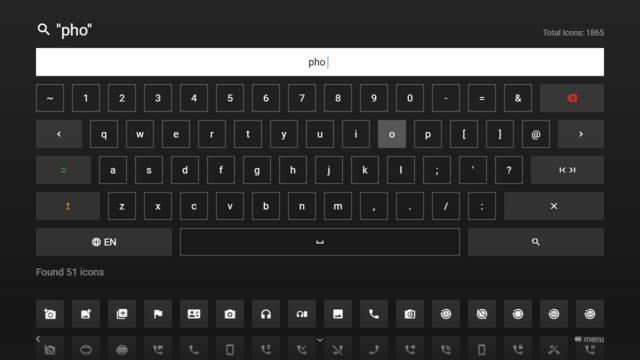
Example[edit]
Screenshot[edit]
Code[edit]
//TODO
Demo[edit]
- Launch via App: https://msx.benzac.de/?start=menu:https://msx.benzac.de/info/xp/data/plugin_test_13.json
- Launch via Demo Page: https://msx.benzac.de/info/?start=content:https://msx.benzac.de/info/xp/data/plugin_test_13.json